Process
Steel cut production
The process steps
-
Cutting procedure
-
Preselection
-
Final classification
-
Dedusting

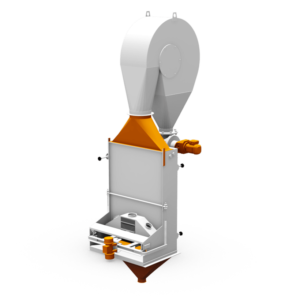
Groat cutter type Krone
Cutting procedure
To manufacture grains cut at right angles to the longitudinal axes, also called steel cut groats, the grain is fed into the machine via an adjustable vibrating trough. The cutting procedure takes place with the aid of two perforated drums and perforated baskets located below them.

Plansifter type EKPS
Preselection
Located in the plansifter are multiple separating sections with sieve stacks. The product falls through an inlet canal onto the first sieve layer. Via circulator vibratory movements of the sieves, various size grades are then sieved out in succession and fed out of the machine via separate outlets.
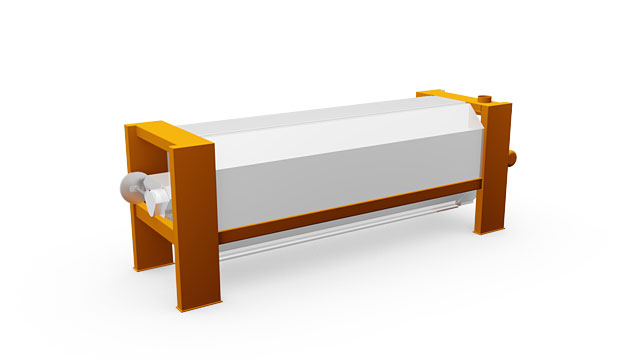
Indent cylinder type ETA
Final classification
The indent cylinder classifies the finely cut and in some cases coarser grains according to length. The rotating indent cylinder shell consists of two half shells, which bear tear-shaped embossings. It is in these embossings that efficient product separation takes place.

Airleg separator with decanter and sluice
Dedusting
In the airleg channel, the upwards-streaming air passes through the resulting product “haze” from the steel cut groats. Here, the parts with a lighter specific weight and adhering pieces of hull are pulled out towards the top. In this step, the last hull and fine particles are removed from the steel cut groats.